| < Previous page | Next page > |
Confluence Zone RefugiaConfluence Thermal Refugia (not scaled and scaled by tributary to mainstem drainage area)
Tool Description: This tool uses the downstream aggregated Current Shade-Thermal Energy parameter (SolMean) and compares the aggregate values at tributary confluences to the aggregate values in mainstem channels (e.g., tributary value - mainstem value) to identify potential tributary sources of cooler water (and also potential sources of warmer tributary water). To provide an index of cool water potential to a mainstem, the result is then multiplied by the ratio of tributary drainage area to mainstem drainage area to provide an index of the relative magnitude of the cooler or warmer water conditions in the mainstem channel.
NOTE, prior to running this tool, you will need to access and process Vegetation Data, such as LEMMA (see Tool).
Please check your dataset, generally these values are pre-calculated during development of the virtual watershed.
Data Type: Line (stream layer)
Field Name: TrbThrm; Common Name: Tributary - Current shade thermal energy MINUS Mainstem - Current shade thermal energy; negative values means that tributaries are potentially providing cooler water while positive values means that tributaries may be contributing warmer water.
Field Name: TrbThrmSc; Common Name: Tributary - Current shade thermal energy MINUS Mainstem - Current shade thermal energy, and then multiplied by the ratio of tributary drainage area to mainstem drainage area; this provides an index that combines TrbThrm with the relative magnitude of tributary flow, this providing information on the relative magnitude of the cooler or water waters.
Units: Watt-hours/m2 and watt-hours/m2 multiplied by tributary drainage area/mainstem drainage area
NetMap Module/Tool: Vegetation/Fire/Climate - Vegetation - Shade/Stream - Thermal Refugia - Confluence Zone Refugia
Model Description: The model predicts thermal energy to stream channels using a combination of bare earth radiation and the effects of current shade conditions on bare earth radiation (See Current Shade-Thermal Energy tool). NetMap aggregates those values downstream (called Along Channel Refugia-Tributary Scale) creating an area weighted, running average based on inherent topographic controls on thermal energy to streams (topographic shading, stream orientation, stream width and solar angle) and the current shade conditions that reduce thermal energy to streams. Then, at each tributary confluence, the downstream aggregated Tributary - Current shade thermal energy is subtracted from the downstream aggregated mainstem Current shade thermal energy (tributary - mainstem). Results with positive values means that the tributary inflow has potentially warmer water temperatures (compared to the mainstem, and thus provides a confluence related thermal refugia) while results with negative values means that the tributary may be contributing cooler water (conditions) compared to the mainstem.
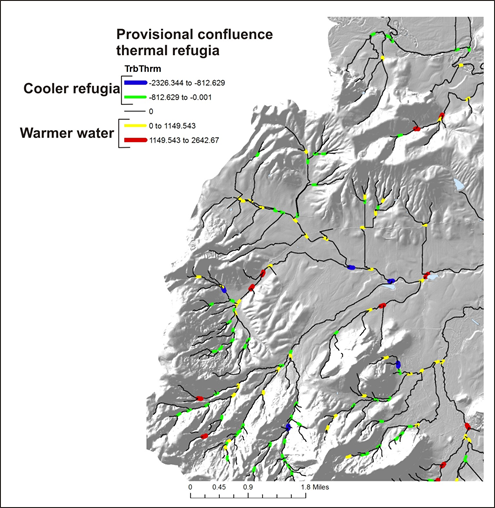 Figure 1. Provisional tributary confluence related thermal refugia; negative numbers represent cooler landscape conditions intersecting warmer landscape condition, in terms of downstream aggregated thermal load.
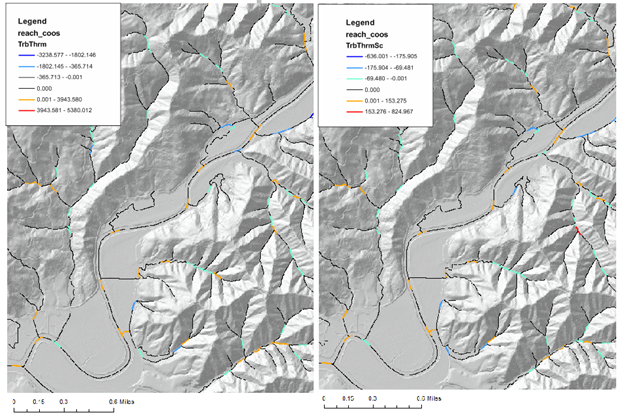 Figure 2. Both types of thermal refugia. (Left) Non-flow scaled. (Right) Flow scaled (multipled by triburary/mainstem).
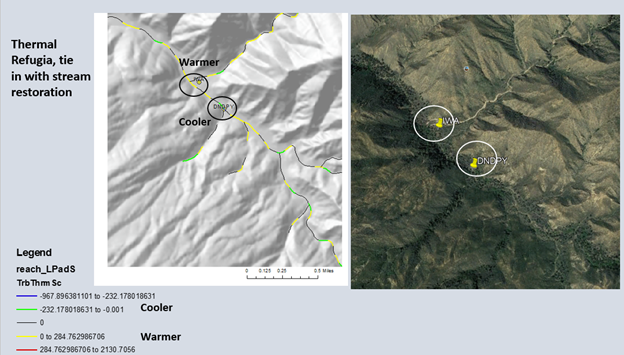 Figure 3. Another example of NetMap's confluence thermal refugia parameter. For best results, use the values scaled by tributary/mainstem drainage area ratio.
|